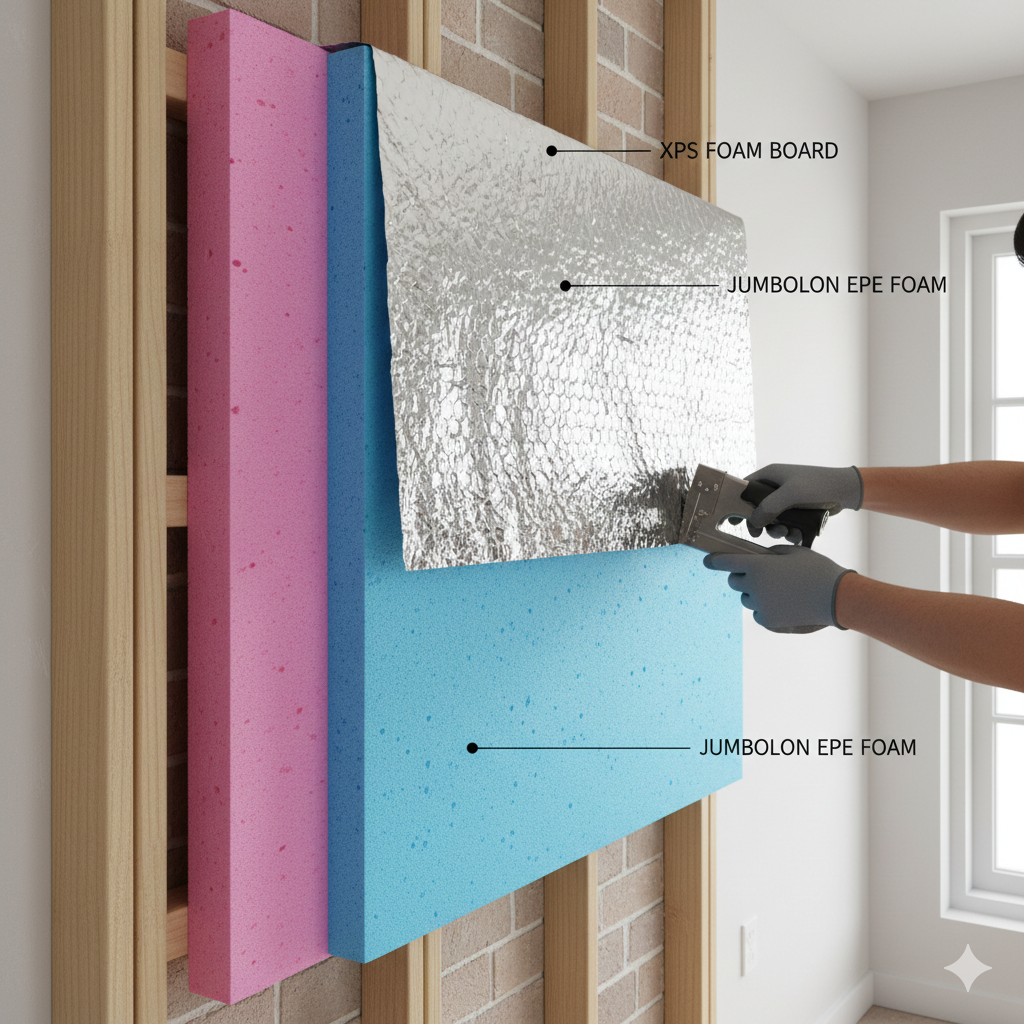
Extreme summer temperatures make indoor comfort a serious challenge, especially in hot and mixed climates. Choosing the right insulation is not only about blocking heat in summer but also managing temperature balance throughout the year. This guide explains which insulation is best for summer heat, how different materials perform, and what works best for walls, interiors, and exteriors.
Why Summer Heat Control Depends on Insulation

Heat enters buildings mainly through roofs, exterior walls, and uninsulated surfaces. Without proper insulation, indoor temperatures rise quickly, increasing reliance on cooling systems. The best heat insulation material reduces heat transfer, improves thermal stability, and maintains comfort without excessive energy use.
Good insulation also works in reverse—helping retain warmth during cooler months—making it useful for both seasonal extremes.
Which Insulation Is Best for Summer Heat in Winter?
Many people assume insulation is only useful for cold climates, but the reality is different.
The same insulation that blocks outdoor heat in summer also prevents indoor warmth from escaping in winter. That’s why which insulation is best for summer heat in winter depends on materials that provide year-round thermal resistance rather than seasonal performance only.
Materials with stable density and air-trapping structures perform best across seasons.
Thermal Insulations Material List

Here is a practical thermal insulations material list commonly used for heat control:
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS)
- Extruded Polystyrene (XPS)
- Rockwool / Mineral Wool
- Polyurethane Foam
- Cellulose Insulation
- Reflective Heat Barriers
Each has different strengths depending on wall type, exposure, and climate.
Best Wall Insulation for Hot Climates

For regions with long summers and intense sun exposure, the best wall insulation for hot climates must slow heat penetration and reduce thermal bridging.
Key requirements include:
- Low thermal conductivity
- Resistance to moisture
- Stable performance at high temperatures
Rigid boards and dense fibrous insulation generally outperform lightweight materials when installed correctly.
Technical Comparison Table – Heat Performance
| Insulation Type | Heat Resistance | Summer Performance | Moisture Resistance | Common Use Areas |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPS Sheets | Medium | Good | Moderate | Walls, ceilings |
| XPS Boards | High | Very Good | High | Roofs, walls |
| Rockwool | High | Very Good | High | Walls, partitions |
| Heat Reflective Sheets | Medium–High | Excellent | High | Roofs, sheds |
| Cellulose Insulation | Medium | Good | Low–Moderate | Interior walls |
Note: Actual performance depends on thickness, density, and installation quality.
Best Insulation for Interior Walls
The best insulation for interior walls focuses on temperature balance rather than direct sun exposure. Interior insulation helps stabilize indoor conditions, reduce heat transfer between rooms, and improve comfort.
Interior wall insulation is especially useful in:
- Multi-storey homes
- Office partitions
- Bedrooms exposed to roof heat
Fibrous and foam-based materials work well when combined with proper sealing.
Best Insulation for Exterior Walls
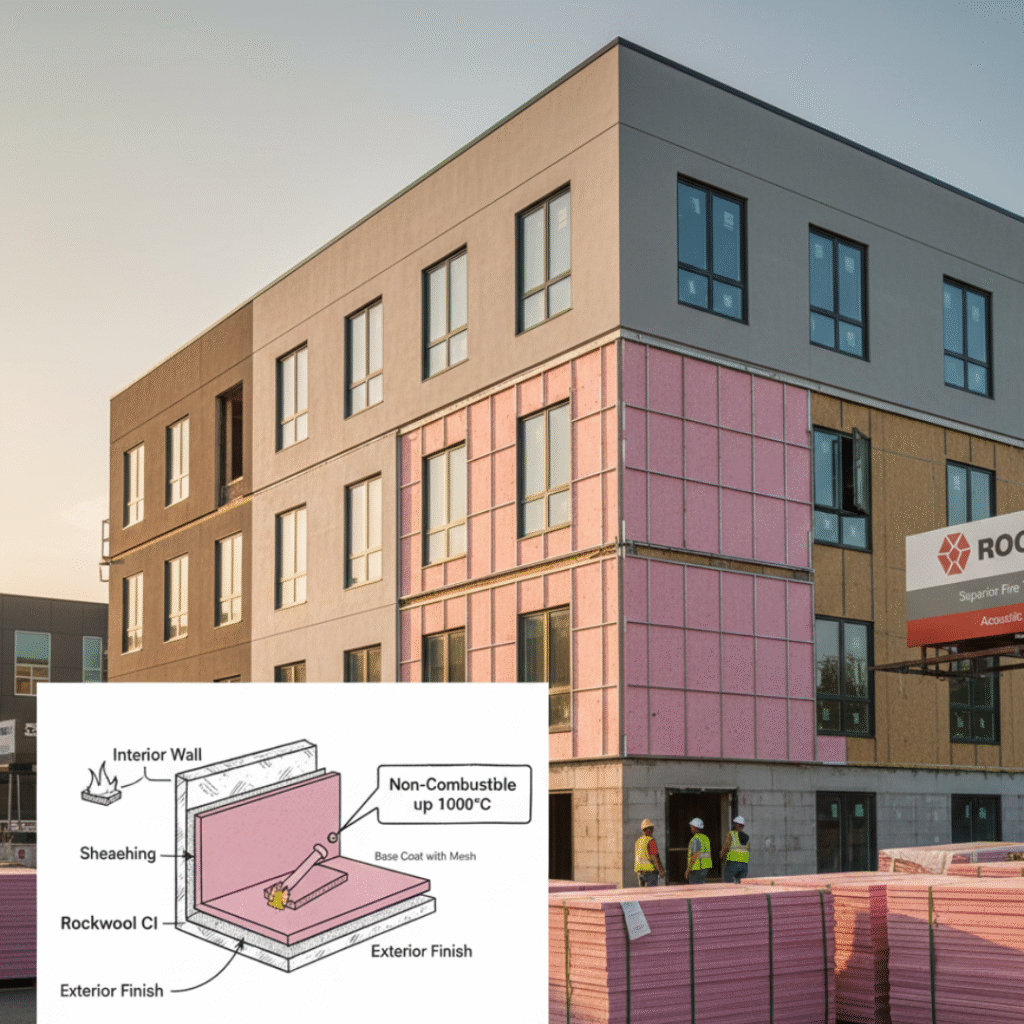
Exterior walls receive direct solar heat for hours each day. The best insulation for exterior walls should resist heat buildup and prevent transfer to indoor spaces.
Exterior insulation systems are effective because they:
- Reduce thermal shock on walls
- Improve overall building envelope efficiency
- Protect structural materials from temperature stress
Continuous insulation layers perform better than isolated patches.
Best Heat Insulation Material: What Actually Works?
There is no single “perfect” insulation, but the best heat insulation material depends on application:
- Roofs need reflective or rigid insulation
- Exterior walls require dense thermal barriers
- Interior spaces benefit from balanced insulation
High-density materials generally slow heat flow more effectively, especially in peak summer conditions.
Cellulose Insulation: Is It Good for Summer Heat?
Cellulose insulation is made from recycled fibers and works by trapping air within its structure. It provides moderate heat resistance and performs best when installed at correct density.
It is commonly used in:
- Wall cavities
- Attic spaces
- Retrofit insulation projects
However, moisture control is important for long-term performance.
Which Insulation Is Best for Summer Heat 2022 vs Today?
Search trends like which insulation is best for summer heat 2022 reflect growing awareness of heat management. Since then, insulation selection has shifted toward higher-performance materials and better installation methods rather than just thickness.
Modern insulation focuses more on:
- Thermal resistance consistency
- Moisture stability
- Long-term durability
How to Choose the Right Insulation for Your Home
When selecting insulation, consider:
- Wall type (interior or exterior)
- Roof exposure
- Climate duration (short vs long summers)
- Budget and lifespan expectations
The right insulation is the one that balances heat resistance, durability, and correct placement.
Final Verdict: Which Insulation Is Best for Summer Heat?
There is no universal answer, but the best results come from combining:
- Proper material selection
- Correct thickness
- Professional installation
Homes in hot climates benefit most from layered insulation strategies rather than relying on a single solution.
FAQ’S
For hot climates, insulation with high thermal resistance and low heat transfer works best. Materials like XPS, rockwool, and reflective heat insulation are commonly preferred for long summer seasons.
The best wall insulation for hot weather is one that slows heat penetration through exterior walls, such as EPS, XPS, or mineral-based insulation installed with proper sealing.
Good insulation works year-round. The same insulation that blocks outdoor heat in summer also helps retain indoor warmth during winter months.
Maximum heat reduction depends on application. Roofs benefit most from reflective or rigid insulation, while walls perform better with dense thermal insulation materials.
Cellulose insulation can reduce heat transfer when installed at the correct density, but it performs best in controlled indoor areas rather than extreme roof exposure.