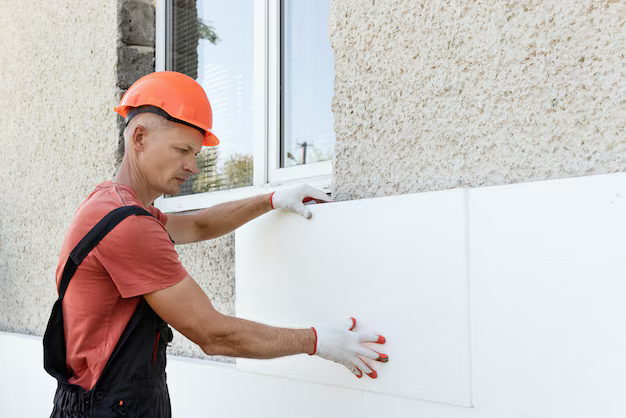
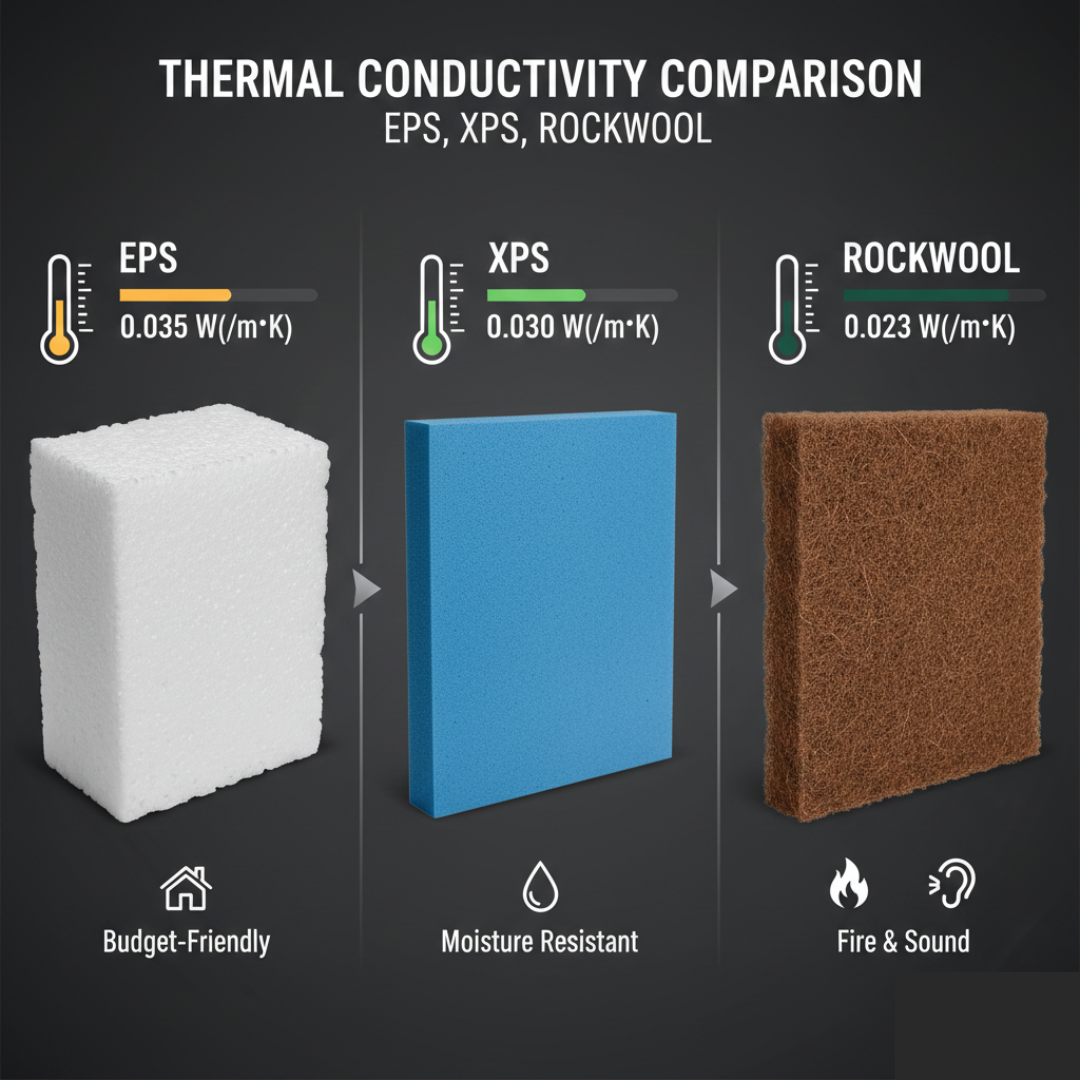
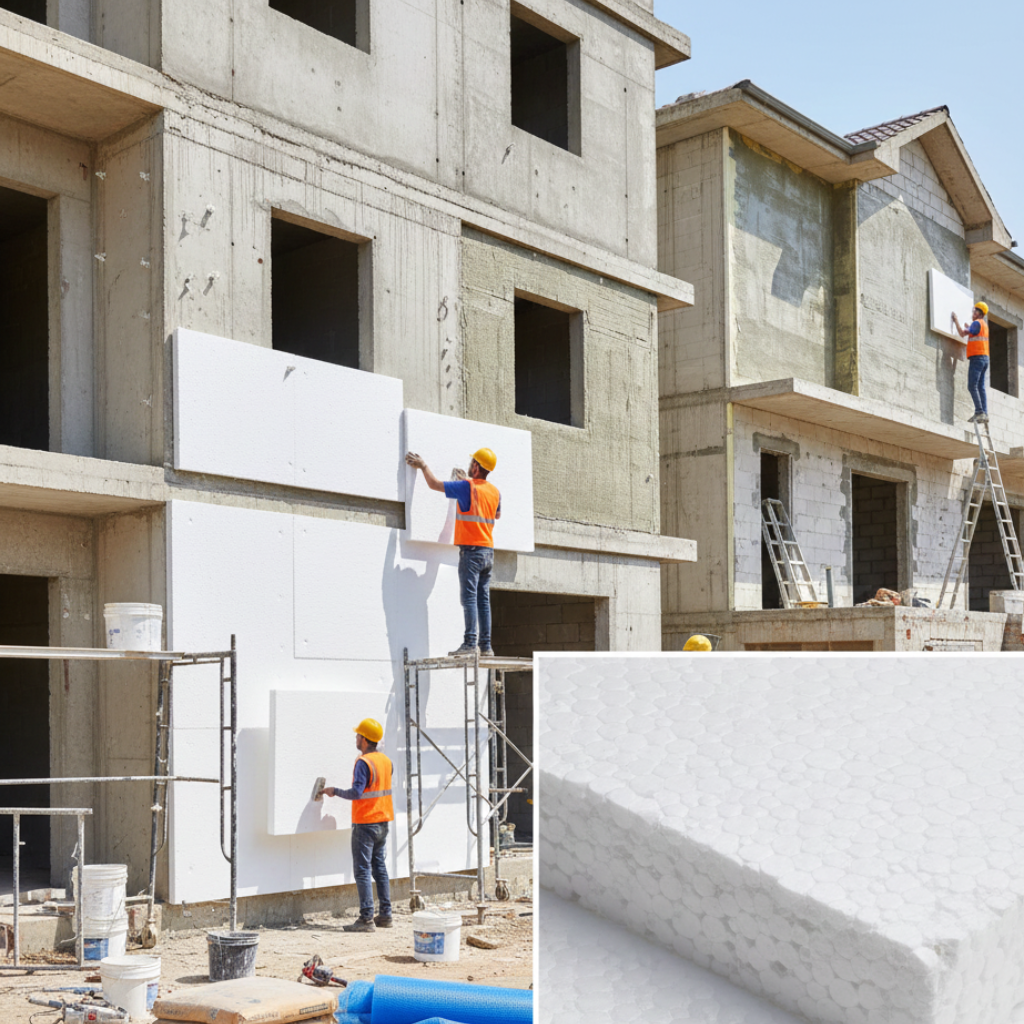
Choosing the right insulation material is a critical decision for residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. Two of the most widely used materials are EPS insulation and rockwool insulation. While both serve the same primary purpose—reducing heat transfer—their composition, performance, and applications differ significantly.
This EPS vs Rockwool – Complete Technical Comparison explains how each material works, where it performs best, and how to decide between them based on thermal, acoustic, moisture, and safety requirements.
Understanding EPS Insulation

EPS insulation (Expanded Polystyrene) is a rigid, lightweight insulation material made by expanding polystyrene beads using steam. The result is a closed-cell structure that traps air, which helps slow down heat transfer.
EPS is widely used in walls, roofs, floors, and foundations due to its affordability and ease of installation.
Key Characteristics of EPS
- Lightweight and easy to handle
- Consistent thermal performance
- Resistant to moisture absorption
- Cost-effective for large surface areas
Understanding Rockwool Insulation

Rockwool insulation is a mineral-based insulation material manufactured by melting volcanic rock and spinning it into dense fibers. This structure makes rockwool excellent for thermal resistance, sound absorption, and fire protection.
Rockwool is commonly used in walls, roofs, industrial plants, and fire-rated structures.
Key Characteristics of Rockwool
- High density and durability
- Excellent fire resistance
- Superior sound absorption
- Vapor-permeable structure
EPS vs Rockwool – Material Composition Comparison

One of the biggest differences in polystyrene vs rockwool insulation lies in how the materials are formed.
EPS relies on trapped air inside rigid foam cells, while rockwool uses intertwined mineral fibers. This structural difference directly impacts performance in heat resistance, sound insulation, and fire behavior.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Both insulation types reduce heat transfer effectively, but in different ways.
- EPS insulation provides stable thermal resistance due to its closed-cell design.
- Rockwool insulation resists heat by slowing conduction through dense mineral fibers.
In standard residential applications, both materials perform efficiently when installed correctly.
EPS vs Rockwool – Technical Comparison Table
| Feature | EPS Insulation | Rockwool Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Expanded Polystyrene | Mineral Wool |
| Thermal Performance | Good | Very Good |
| Fire Resistance | Limited (needs protection) | Excellent (non-combustible) |
| Sound Insulation | Low to Medium | High |
| Moisture Resistance | Good | Moderate |
| Breathability | Low | High |
| Density Range | 10–30 kg/m³ | 40–120 kg/m³ |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Installation Ease | Easy | Moderate |
| Common Applications | Walls, roofs, floors | Fire-rated walls, partitions, ducts |
| Cost Level | Economical | Higher than EPS |
| Suitability for Pakistan Climate | Very Suitable | Suitable for premium projects |
EPS vs XPS – Where EPS Stands
When discussing eps vs xps, EPS is generally more breathable and flexible in vapor movement, while XPS offers higher compressive strength. EPS remains popular for walls and roofs where breathability and cost-efficiency are priorities.
Fire Resistance and Safety
Fire performance is a major consideration in insulation selection.
- Rockwool insulation is non-combustible and can withstand extremely high temperatures.
- EPS is combustible but often treated with fire-retardant additives to slow flame spread.
For fire-rated walls or industrial environments, rockwool is typically preferred.
Sound Insulation Performance
In polystyrene vs rockwool sound insulation, rockwool clearly outperforms EPS.
- Rockwool absorbs airborne and impact sound due to its fibrous structure.
- EPS primarily reflects sound rather than absorbing it.
For noise-sensitive spaces such as apartments, offices, or studios, rockwool offers better acoustic comfort.
Moisture Behavior & Breathability
A common question is: is EPS insulation breathable?
EPS allows limited vapor diffusion while resisting liquid water absorption. This makes it suitable for controlled indoor environments.
Rockwool, on the other hand, is vapor-permeable and helps regulate moisture while remaining water-repellent. This characteristic makes it suitable for buildings that require breathability without trapping moisture.
Installation & Handling Comparison
- EPS insulation is easy to cut, lightweight, and quick to install, reducing labor time.
- Rockwool is heavier and requires protective handling but offers greater structural stability in vertical applications.
Environmental & Longevity Considerations
Rockwool is manufactured from natural minerals and is dimensionally stable over time. EPS is long-lasting and recyclable but derived from petrochemical sources.
Both materials have long service lives when installed properly.
Where EPS Is the Better Choice
EPS is ideal for:
- Budget-sensitive projects
- External wall insulation systems
- Roof and floor insulation
- Applications requiring lightweight materials
Where Rockwool Is the Better Choice

Rockwool is better suited for:
- Fire-rated walls and ceilings
- Soundproofing applications
- High-temperature environments
- Industrial and commercial buildings
Final Verdict: EPS vs Rockwool
There is no single “best” insulation—only the right one for your project.
- Choose EPS insulation for affordability, ease of installation, and thermal efficiency.
- Choose rockwool insulation when fire safety, sound insulation, and breathability are critical.
Understanding the technical differences between these materials ensures better energy efficiency, comfort, and long-term performance.
FAQ’S
The main difference lies in composition and performance. EPS insulation is made from expanded polystyrene and focuses on thermal efficiency, while rockwool insulation is made from mineral fibers and offers superior fire resistance and sound absorption.
For wall insulation in Pakistan, EPS is commonly used for residential projects due to affordability and thermal performance. Rockwool is preferred in commercial or industrial buildings where fire safety and acoustic insulation are critical.
EPS insulation is not fully breathable. It has low vapor permeability, which helps block moisture but requires proper ventilation design to avoid condensation buildup inside walls.
Yes. Rockwool performs significantly better in sound control. This is why polystyrene vs rockwool sound insulation comparisons often favor rockwool for apartments, offices, and studios.
When comparing EPS vs XPS, XPS offers higher compressive strength and moisture resistance, while EPS is more cost-effective and widely used for wall and roof insulation.
Rockwool is non-combustible and can withstand very high temperatures, making it safer in fire-rated applications. EPS must be protected with fire-resistant layers when used in building envelopes.