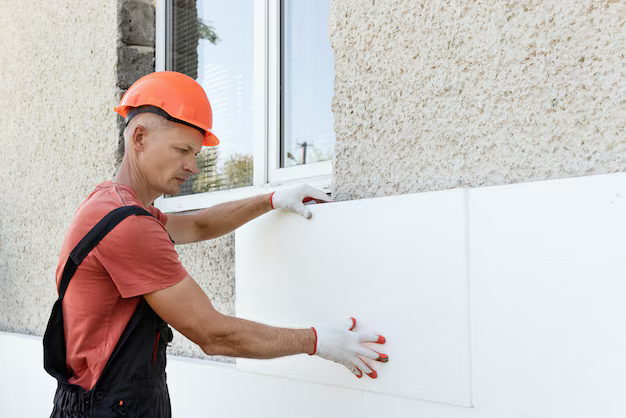
Insulation materials play a critical role in maintaining energy efficiency, controlling indoor temperature, and reducing utility costs. With numerous types of insulation available, it can be overwhelming to choose the right one for your project. In this blog, we present a Full Comparison Chart of All Insulation Materials in Pakistan, helping you make an informed decision. We will also discuss the thermal conductivity of all insulation materials and identify the best insulation board for roof applications.
What is Insulation Material?
Insulation materials are substances used in buildings to reduce heat transfer, sound, or vibration in Pakistan. They help maintain comfortable indoor temperatures while minimizing energy consumption. Different insulation materials have unique properties, including density, thermal resistance, and moisture resistance, which make them suitable for specific applications.
Importance of Choosing the Right Insulation
Selecting the right insulation material affects:
- Energy Efficiency: Proper insulation reduces heating and cooling costs.
- Comfort: Maintains a consistent indoor temperature.
- Noise Reduction: Certain insulation materials provide excellent acoustic control.
- Durability: High-quality insulation extends the lifespan of your building structure.
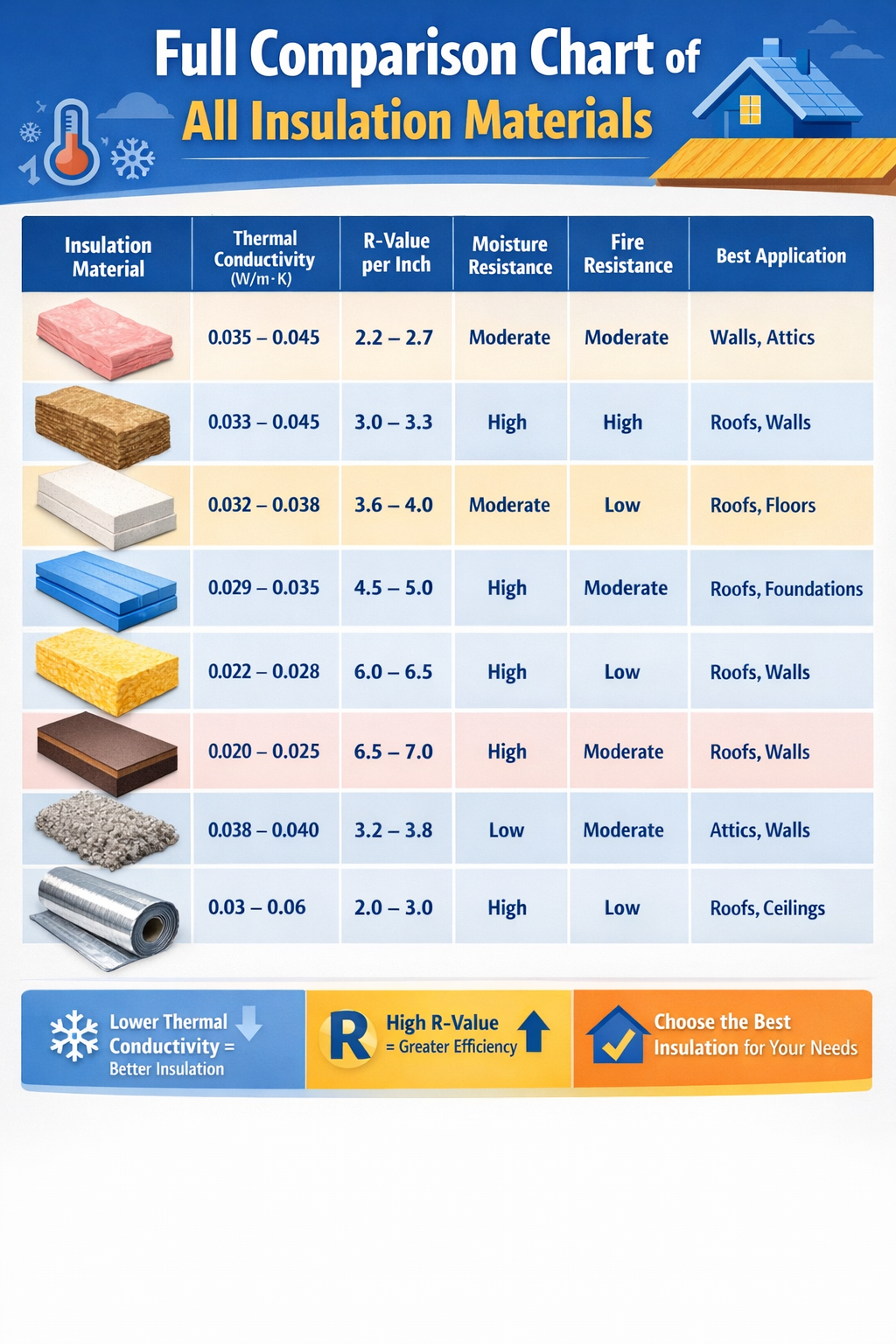
The Full Comparison Chart of All Insulation Materials below summarizes these aspects to simplify your choice.
Full Comparison Chart of All Insulation Materials
| Insulation Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | R-Value per Inch | Moisture Resistance | Fire Resistance | Best Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiberglass | 0.035 – 0.045 | 2.2 – 2.7 | Moderate | Moderate | Walls, Attics |
| Mineral Wool | 0.033 – 0.045 | 3.0 – 3.3 | High | High | Roofs, Walls |
| Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) | 0.032 – 0.038 | 3.6 – 4.0 | Moderate | Low | Roofs, Floors |
| Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) | 0.029 – 0.035 | 4.5 – 5.0 | High | Moderate | Roofs, Foundations |
| Polyurethane Foam (PU) | 0.022 – 0.028 | 6.0 – 6.5 | High | Low | Roofs, Walls |
| Phenolic Foam | 0.020 – 0.025 | 6.5 – 7.0 | High | Moderate | Roofs, Walls |
| Cellulose | 0.038 – 0.040 | 3.2 – 3.8 | Low | Moderate | Attics, Walls |
| Reflective Foil | 0.03 – 0.06 | 2.0 – 3.0 | High | Low | Roofs, Ceilings |
This Full Comparison Chart of All Insulation Materials allows homeowners, contractors, and architects to evaluate materials based on thermal conductivity of all insulation materials and other critical properties.
Thermal Conductivity of All Insulation Materials
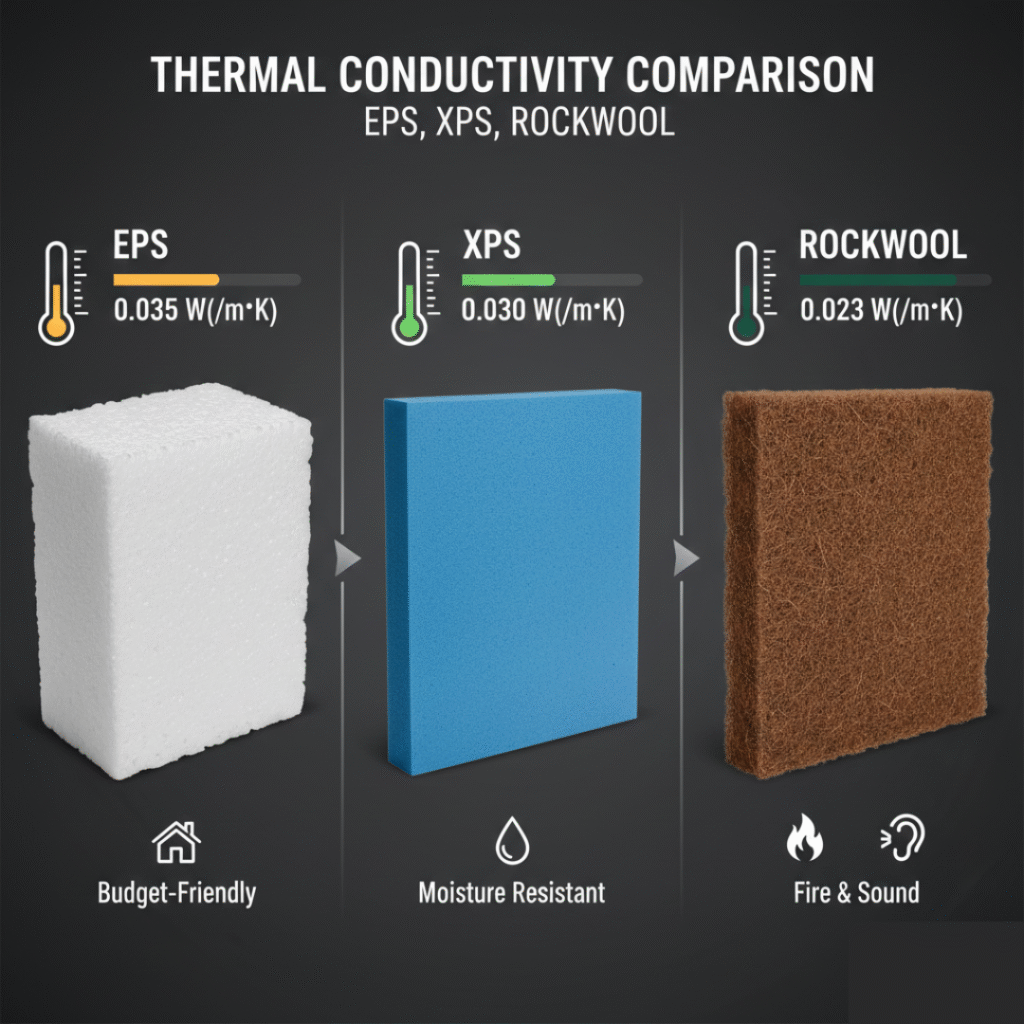
Thermal conductivity measures how well a material conducts heat. Lower values indicate better insulation performance. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Fiberglass: 0.035 – 0.045 W/m·K, suitable for walls and attics.
- Mineral Wool: 0.033 – 0.045 W/m·K, excellent for fire-resistant applications.
- EPS & XPS: 0.029 – 0.038 W/m·K, perfect for roofs and foundations.
- PU & Phenolic Foam: 0.020 – 0.028 W/m·K, among the most efficient insulators.
- Cellulose: 0.038 – 0.040 W/m·K, eco-friendly and cost-effective.
- Reflective Foil: 0.03 – 0.06 W/m·K, best for radiant heat reflection.
Understanding the thermal conductivity of all insulation materials helps determine the R-value needed for your specific building requirements in Pakistan.
Best Insulation Board for Roof
When it comes to roofing, you need materials that offer:
- Low thermal conductivity
- Moisture resistance
- Durability against weather conditions
Based on these factors, the best insulation board for roof applications are:
- Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) – Highly moisture-resistant and strong.
- Polyurethane (PU) Foam Board – Exceptional thermal performance and lightweight.
- Phenolic Foam Board – Superior insulation with a high R-value per inch.
These boards ensure your roof stays cool in summer and warm in winter, improving energy efficiency and reducing long-term costs.
How to Choose the Right Insulation
Consider these factors before selecting an insulation material:
- Purpose: Walls, roofs, floors, or attics.
- Climate: Hot, cold, or humid regions.
- Budget: Initial cost vs. long-term energy savings.
- Environmental Impact: Recyclable and eco-friendly options.
- Fire and Moisture Resistance: Essential for safety and durability.
Using the Full Comparison Chart of All Insulation Materials will simplify this selection process.
Conclusion
Choosing the right insulation material is critical for building comfort, energy efficiency, and safety. The Full Comparison Chart of All Insulation Materials presented here, along with details about thermal conductivity of all insulation materials and the best insulation board for roof, helps you make a well-informed decision.
Invest wisely in insulation today, and enjoy lower energy bills, better comfort, and a sustainable home for years to come.
FAQ’S
For hot climates, materials with low thermal conductivity like PU foam, XPS, and Phenolic foam are ideal, as they reduce heat transfer and keep interiors cooler.
The best insulation board for roof applications depends on moisture resistance, thermal efficiency, and durability. XPS, PU foam, and Phenolic boards are excellent options.
EPS (Expanded Polystyrene) has slightly higher thermal conductivity and lower moisture resistance than XPS (Extruded Polystyrene), making XPS more suitable for roofing and foundations.
Thermal conductivity indicates how well a material resists heat flow. Lower thermal conductivity means better insulation performance, reducing energy costs and maintaining comfort.
Yes, reflective foil is ideal for roofs, ceilings, and walls where radiant heat reflection is important. It works best in combination with other insulation materials for maximum efficiency.