Choosing the right insulation is one of the most important decisions when designing or upgrading a home. In hot and mixed climates like Pakistan, insulation directly affects indoor comfort, electricity bills, and long-term building durability. Two of the most commonly compared options are XPS insulation and Glasswool insulation. This guide explains their differences in a clear, practical way to help homeowners make an informed decision.
Understanding Home Insulation Needs in Pakistan

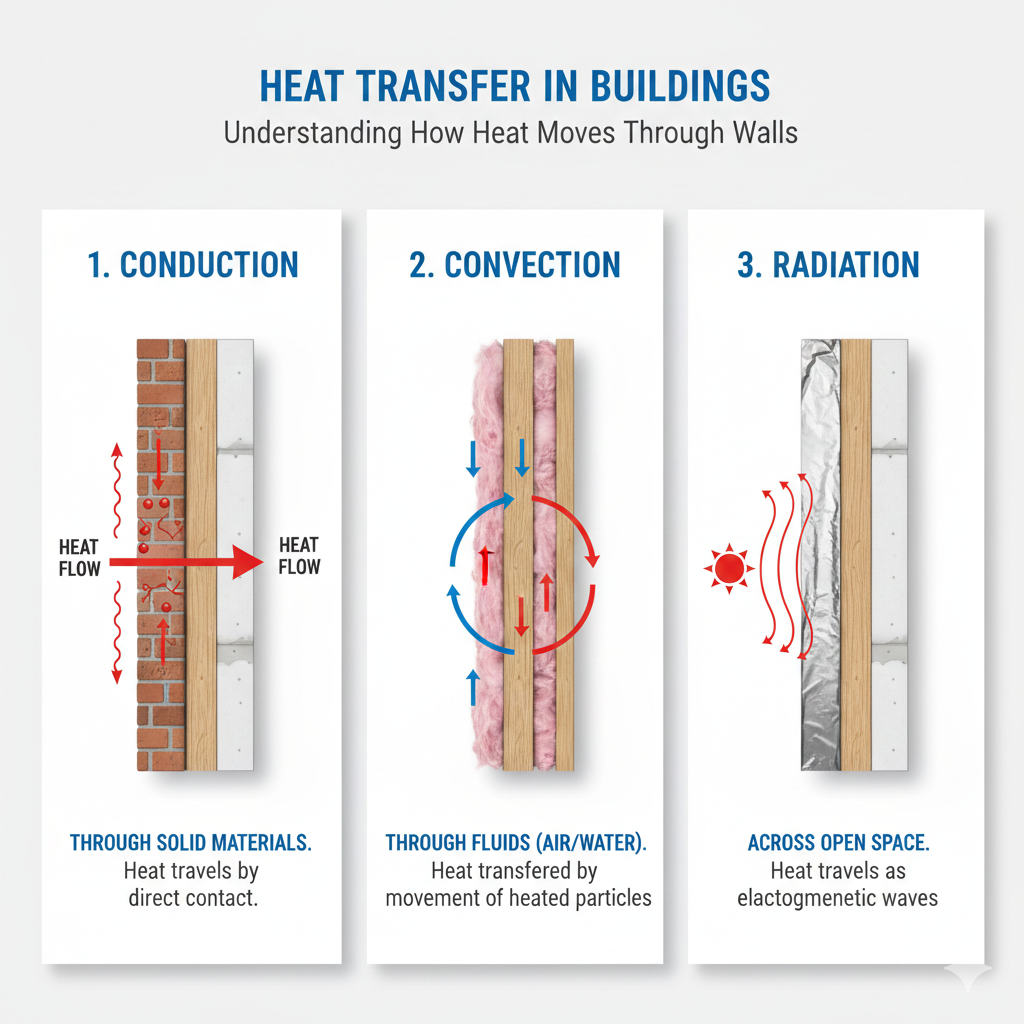
Homes in Pakistan face intense heat, humidity variations, and rising energy costs. Effective insulation slows down heat transfer, reduces indoor temperature fluctuations, and supports energy efficiency. Whether the goal is roof protection, wall insulation in Pakistan, or overall thermal performance, material selection plays a critical role.
What Is XPS Insulation?
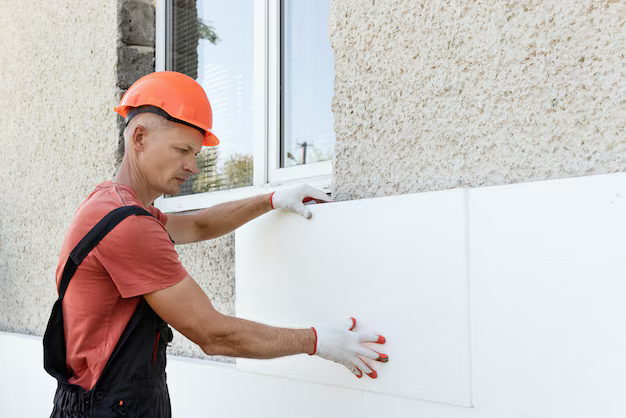
XPS insulation, made from extruded polystyrene, is a rigid board designed to resist heat, moisture, and pressure. Due to its closed-cell structure, XPS material offers consistent thermal performance even in demanding environments.
Key Characteristics of XPS Insulation
- High compressive strength
- Low water absorption
- Long service life
- Suitable for roofs, floors, and external walls
Because of its durability, XPS insulation is commonly used in residential and commercial construction across Pakistan.
What Is Glasswool Insulation?

Glasswool insulation is produced from recycled glass fibers arranged into soft, flexible mats or rolls. It traps air between fibers, which slows heat movement and improves acoustic comfort.
Key Characteristics of Glasswool
- Lightweight and flexible
- Good thermal and sound insulation
- Commonly used in ceilings and cavity walls
- Requires proper sealing to avoid moisture issues
Glasswool is often compared with alternatives like rockwool insulation, which uses stone fibers instead of glass.
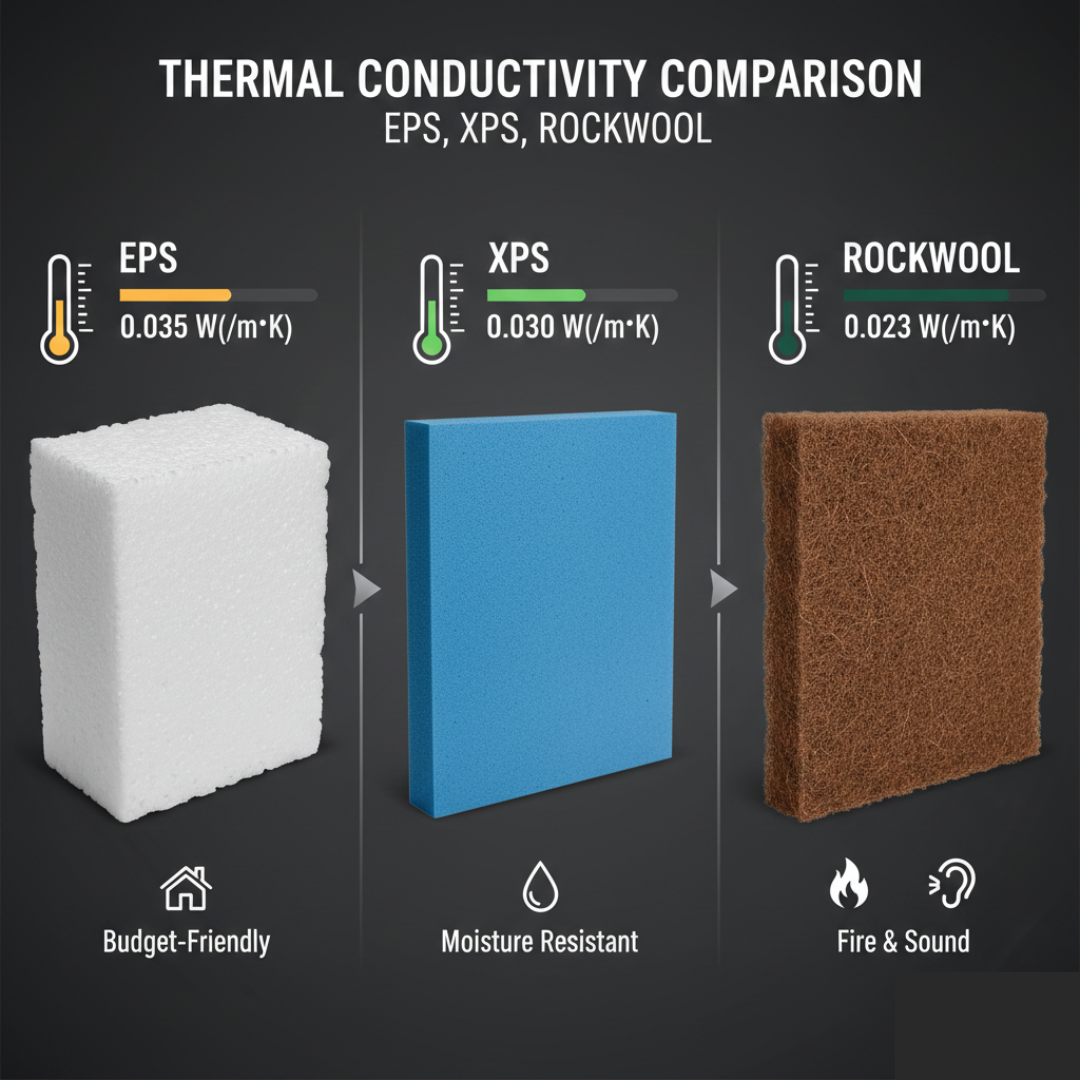
XPS vs Glasswool vs Rockwool – Detailed Comparison Table
| Feature | XPS Insulation | Glasswool Insulation | Rockwool Insulation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Extruded polystyrene board | Glass fiber mat | Stone fiber slab |
| Thermal Performance | High & stable | Good (may reduce if compressed) | High |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent | Low to medium | Medium |
| Structural Strength | High (load-bearing) | Low | Medium |
| Fire Resistance | Moderate | Moderate | Excellent |
| Application Areas | Roofs, floors, walls | Ceilings, partitions | Walls, fire-rated zones |
| Suitability for Homes | Very suitable | Suitable (indoor use) | Limited residential use |
| Maintenance Need | Low | Medium | Low |
| Cost Range | Medium to high | Low to medium | High |
Summary:
For long-term residential use in Pakistan’s climate, XPS offers the best balance of durability, moisture resistance, and thermal efficiency.
XPS vs Glasswool: Core Performance Comparison

Thermal Efficiency
XPS provides stable insulation values over time due to its closed-cell structure. Glasswool performs well initially but may lose effectiveness if compressed or exposed to moisture.
Moisture Resistance
XPS boards resist water penetration, making them suitable for humid climates. Glasswool requires vapor barriers to maintain performance.
Structural Strength
XPS can handle load-bearing applications such as floors. Glasswool is not designed for pressure-bearing use.
XPS vs Polyiso and Mineral Wool Comparisons
When evaluating insulation, homeowners often explore related comparisons like XPS vs polyiso or XPS ve mineral wool. Polyiso offers high thermal resistance but may lose efficiency in extreme heat. Mineral wool, including rockwool, excels in fire resistance but is heavier and costlier.
These comparisons highlight why XPS remains a balanced option for many residential applications.
Role of Rockwool in Home Insulation

Rockwool insulation is known for fire resistance and sound absorption. While effective, it is usually preferred in industrial or high-rise buildings rather than standard homes due to installation complexity and weight. Rockwool is often chosen when fire safety is prioritized over cost.
Cost Considerations for Homeowners
Insulation cost varies depending on material type, thickness, and location. While XPS boards may have a higher upfront price, they often deliver better long-term value due to durability. Products like jumbolon sheet price in Pakistan are also considered by homeowners seeking flexible insulation solutions, but they serve different use cases than rigid XPS boards.
Which Insulation Is Better for Homes?
Choose XPS Insulation If:
- You need moisture-resistant insulation
- Roof or floor insulation is required
- Long-term durability is a priority
Choose Glasswool If:
- Budget is limited
- Insulation is needed for ceilings or partitions
- Sound insulation is also important
For most modern homes, especially those focused on energy efficiency and structural reliability, XPS insulation is often the preferred solution.
Final Verdict
There is no universal insulation solution for every home. However, when comparing durability, moisture resistance, and performance stability, XPS consistently outperforms Glasswool for long-term residential use. Homeowners should evaluate climate, installation area, and budget before making a final decision.
FAQ’S
XPS insulation is generally better for wall insulation in Pakistan because it resists moisture and maintains thermal performance in hot and humid conditions.
Yes, Glasswool insulation is suitable for ceilings and internal partitions, especially where sound insulation is also required. However, it needs proper sealing against moisture.
XPS focuses on thermal efficiency and moisture resistance, while rockwool insulation provides superior fire resistance. Rockwool is often used in commercial or industrial projects.
Yes, XPS insulation reduces heat transfer through roofs and walls, helping maintain indoor temperature and lowering air-conditioning usage.