Underfloor heating systems are becoming increasingly popular in modern residential and commercial construction due to their comfort, energy efficiency, and space-saving design. However, the success of any underfloor heating setup depends heavily on the insulation layer installed beneath it. This is where EPS and XPS insulation boards play a critical role.
This guide explains how EPS and XPS perform in underfloor heating applications, compares their thermal and structural properties, and helps you select the most suitable material for long-term efficiency.
Understanding Underfloor Heating Insulation
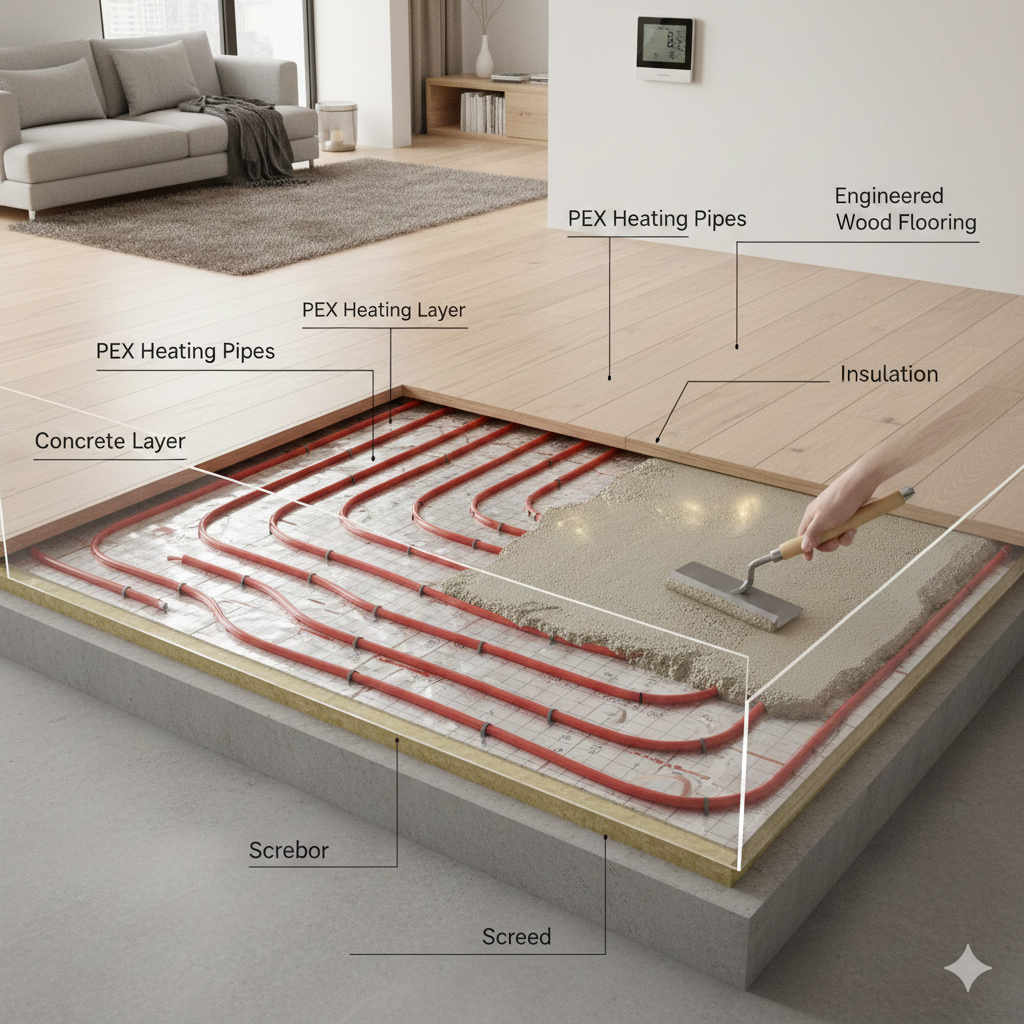
Underfloor heating works by evenly distributing heat across a floor surface. Without proper insulation below the heating pipes or cables, a significant amount of heat is lost downward into the slab or soil. High-quality insulation ensures:
- Faster heat response
- Reduced energy consumption
- Consistent indoor temperatures
- Protection of heating elements
Choosing between EPS and XPS insulation directly impacts system performance and operating cost.
Best EPS & XPS for Underfloor Heating Systems

The best EPS & XPS for Underfloor Heating Systems depends on structural load, moisture exposure, and insulation thickness requirements. Both materials are rigid foam boards, but their internal structure gives them different advantages.
EPS is lightweight and economical, while XPS is dense and moisture-resistant. Each serves a distinct purpose in underfloor applications.
EPS vs XPS Thermal Conductivity

EPS vs XPS Thermal Conductivity is one of the most important performance comparisons.
- EPS has a slightly higher thermal conductivity, meaning it allows marginally more heat transfer.
- XPS offers lower thermal conductivity, which improves heat retention under floors.
For projects where maximum thermal efficiency is required in limited thickness, XPS is generally preferred.
EPS Vs XPS R-Value Explained
The EPS Vs XPS R-Value comparison helps determine insulation effectiveness per inch.
- EPS provides stable R-values that depend on density.
- XPS delivers higher R-values per thickness, making it suitable for compact floor assemblies.
In underfloor heating, higher R-value insulation improves system efficiency by directing heat upward instead of allowing it to escape into the slab.
EPS Vs XPS Insulation Performance Under Floors

When comparing EPS Vs XPS Insulation, performance differences become more noticeable in underfloor heating environments:
- EPS performs well in dry, low-load residential floors.
- XPS excels in high-load, moisture-prone, or commercial floors.
Both materials are compatible with hydronic and electric heating systems when correctly installed.
EPS vs XPS Cost Comparison
From a budgeting perspective, EPS vS XPS Cost is often a deciding factor.
- EPS is significantly more affordable and ideal for large-area residential projects.
- XPS costs more upfront but offers longer lifespan and improved durability.
For developers working within tight budgets, EPS provides excellent value, while XPS is better for premium or long-term projects.
EPS vs XPS Compressive Strength
EPS vs XPS Compressive Strength is critical for underfloor heating systems installed beneath concrete slabs.
- EPS offers moderate compressive strength, sufficient for homes.
- XPS provides high compressive strength, making it suitable for heavy loads, machinery, and commercial flooring.
This makes XPS more reliable for under-slab insulation in demanding environments.
Role of XPS Insulation in Heated Floors

XPS Insulation is widely used in modern underfloor heating systems due to its closed-cell structure. It resists moisture absorption, maintains shape under load, and ensures consistent thermal performance over time.
These properties make XPS particularly effective in basements, ground floors, and high-traffic areas.
EPS vs XPS Under Slab Applications
The EPS vs XPS under slab comparison highlights suitability for different ground conditions.
- EPS is suitable for dry soil conditions with controlled loads.
- XPS performs better in wet soil, high water table areas, or where structural pressure is high.
Selecting the correct material ensures long-term insulation performance and prevents heat loss beneath the slab.
Which Insulation Is Better for Underfloor Heating?
There is no universal answer, as the best choice depends on application:
- Choose EPS for residential homes, apartments, and cost-sensitive projects.
- Choose XPS for commercial buildings, industrial floors, and moisture-exposed slabs.
Both materials can deliver excellent underfloor heating performance when properly designed.
Installation Best Practices
For optimal results:
- Ensure boards are tightly fitted with no gaps
- Install a vapor barrier if required
- Place heating pipes or cables evenly
- Pour concrete carefully to avoid board displacement
Correct installation is just as important as material selection.
EPS & XPS for Underfloor Heating Systems – (2026)
Prices vary by density, thickness, and city. Below are market-realistic ranges used by insulation suppliers in Pakistan.
| Material | Thickness | Approx. Price Range (PKR / sq.ft) | Best Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| EPS Sheet | 1 inch | 160 – 220 | Residential underfloor heating |
| EPS Sheet | 2 inch | 280 – 360 | Under slab insulation (homes) |
| XPS Insulation Board | 25mm | 380 – 520 | High-efficiency heated floors |
| XPS Insulation Board | 50mm | 650 – 850 | Commercial & moisture-prone slabs |
Cost Insight:
EPS remains the economical choice, while XPS justifies its higher price with better thermal resistance, compressive strength, and moisture stability.
Final Thoughts
EPS and XPS insulation boards both play a vital role in underfloor heating systems. Understanding their differences in thermal performance, cost, and strength allows homeowners and builders to make informed decisions that improve comfort and energy efficiency.
Choosing the right insulation today ensures lower heating costs and better performance for years to come.
FAQ’S
Both work well, but XPS is better for moisture resistance and high loads, while EPS is ideal for cost-effective residential underfloor heating systems.
Typically, 25mm to 50mm insulation is recommended depending on slab type, load, and desired thermal performance.
Yes. EPS works well in dry regions, while XPS is recommended in humid cities like Karachi due to its water resistance.
Lower thermal conductivity means less heat loss. XPS generally performs better, improving heating efficiency and reducing energy bills.
Yes. EPS vs XPS compressive strength becomes critical under concrete slabs. XPS handles higher structural loads more effectively.
